マルビジン
| マルビジン | |
|---|---|
| |
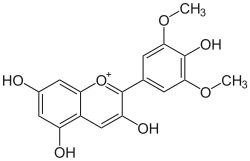
3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy- 3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)chromenium | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 643-84-5 |
| PubChem | 159287 |
| ChemSpider | 140095 |
| 日化辞番号 | J244.836J |
| KEGG | C08716 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL255753 |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C17H15O7+ |
| モル質量 | 331.2968 g/mol |
| 精密質量 | 331.081778 |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
マルビジン (Malvidin) は、O-メチル化アントシアニジンの一種である。主要な植物色素として、その配糖体は自然界に広く存在する。
自然界での存在[編集]
マルビジンは、サクラソウ属の青色の花弁の色素となっている。ルリハコベの青色の花にもマルビジンが高含量で含まれている。
また、ヨーロッパブドウにも含まれ、赤ワインの色の主な原因にもなっている[1]。チョコベリーやジューンベリー等のベリー類にも含まれる[2][3]。
化学[編集]
マルビジンの弱酸性や中性の溶液は赤色であるのに対し、塩基性の溶液は青色である。
マルビジンを分解するとシリング酸を遊離する。また、アントシアノンAも酸性条件下でのマルビジンの分解生成物である[4][5]。
考古学のマーカーとしての利用[編集]
古代エジプトの飲料shedehのかめにマルビジンが分解されて遊離するシリング酸が残っていることが発見された。また、アルメニアで2007年に発見された、アレニの6100年前のワイナリーでもマルビジンの存在が発見された。
配糖体[編集]
- マルビン:マルビジンのジグルコシド
- オエニン:マルビジンの3-グルコシド
- プリムリン:マルビジンの3-O-ガラクトシド
- マルビジン 3-ルチノシド:クルクマ・シャロームの苞葉の色素[6]
- マルビジン 3-O-グルコシド-5-O-(6-アセチルグルコシド):フウロソウ属の青色の色素[7]
出典[編集]
- ^ “Phytochemicals: Malvidin”. Top Cultures. 2009年5月20日閲覧。
- ^ Mazza G (2005). “Compositional and functional properties of saskatoon berry and blueberry”. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 5 (3): 99-118.
- ^ Bakowska-barczak (2007). “Survey of bioactive components in Western Canadian berries”. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 85 (11): 1139-52. doi:10.1139/y07-102. PMID 18066116.
- ^ Anthocyanone A: a quinone methide derivative resulting from malvidin 3-O-glucoside degradation. Lopes P, Richard T, Saucier C, Teissedre PL, Monti JP and Glories Y, J Agric Food Chem., 2007 Apr 4, 55(7), pages 2698-2704, PMID 17338545
- ^ How wine polyphenols evolve during wine ageing? by Cedric Saucier
- ^ Malvidin 3-rutinoside as the pigment responsible for bract color in Curcuma alismatifolia. Nakayama M, Roh MS, Uchida K, Yamaguchi Y, Takano K and Koshioka M, Biosci Biotechnol Biochem., 2000 May, 64(5), pages 1093-1095, PMID 10879491
- ^ Malvidin-3-O-glucoside-5-O-(6-acetylglucoside) and its colour manifestation in 'Johnson's Blue' and other 'blue' geraniums. Markham K.R., Mitchell K.A. and Boase M.R., Phytochemistry, 1997, Volume 45, pages 417-423, doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(96)00831-X
