「メベンダゾール」の版間の差分
編集の要約なし |
en:Mebendazole(2016年4月2日 土曜日 13:53:40(UTC))を翻訳。 |
||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
{{Drugbox |
{{Drugbox |
||
| Verifiedfields = changed |
|||
| verifiedrevid = 457797273 |
| verifiedrevid = 457797273 |
||
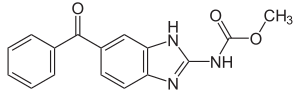
| IUPAC_name = methyl (5-benzoyl-1''H''-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate |
| IUPAC_name = methyl (5-benzoyl-1''H''-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate |
||
| image = Mebendazol.svg |
| image = Mebendazol.svg |
||
| width = 300 |
| width = 300 |
||
<!--Clinical data--> |
<!--Clinical data--> |
||
| tradename = Vermox<ref>{{Cite book|last1=Ebadi|first1=Manuchair|title=Desk reference of clinical pharmacology|date=2008|publisher=CRC Press|location=Boca Raton|isbn=9781420047448|page=403|edition=2|url=https://books.google.ca/books?id=ihxyHbnj3qYC&pg=PA403}}</ref> |
|||
| tradename = |
|||
| Drugs.com = {{ |
| Drugs.com = {{Drugs.com|monograph|mebendazole}} |
||
| MedlinePlus = a682315 |
| MedlinePlus = a682315 |
||
| pregnancy_AU = B3 |
|||
| pregnancy_category = C |
|||
| |
| pregnancy_US = C |
||
| legal_AU = S2 |
|||
| legal_CA = OTC |
|||
| legal_UK = GSL |
|||
| legal_US = Rx-only |
|||
| routes_of_administration = Oral |
| routes_of_administration = Oral |
||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
||
| bioavailability = |
| bioavailability = 2-10% |
||
| protein_bound = 95% |
|||
| metabolism = Hepatic |
| metabolism = [[肝臓|Hepatic]] (extensive) |
||
| elimination_half-life = |
| elimination_half-life = 3-6 hours |
||
| excretion = |
| excretion = Faeces, urine (5-10%) |
||
<!--Identifiers--> |
<!--Identifiers--> |
||
| |
| CAS_number_Ref = {{Cascite|correct|??}} |
||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} |
|||
| CAS_number = 31431-39-7 |
| CAS_number = 31431-39-7 |
||
| ATC_prefix = P02 |
| ATC_prefix = P02 |
||
| 28行目: | 28行目: | ||
| ATC_supplemental = {{ATCvet|P52|AC09}} |
| ATC_supplemental = {{ATCvet|P52|AC09}} |
||
| PubChem = 4030 |
| PubChem = 4030 |
||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite| |
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} |
||
| DrugBank = |
| DrugBank = DB00643 |
||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{ |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{Chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| ChemSpiderID = 3890 |
| ChemSpiderID = 3890 |
||
| UNII_Ref = {{ |
| UNII_Ref = {{Fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
||
| UNII = 81G6I5V05I |
| UNII = 81G6I5V05I |
||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} |
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} |
||
| KEGG = D00368 |
| KEGG = D00368 |
||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ |
| ChEBI_Ref = {{Ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
||
| ChEBI = 6704 |
| ChEBI = 6704 |
||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ |
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{Ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
||
| ChEMBL = 685 |
| ChEMBL = 685 |
||
<!--Chemical data--> |
<!--Chemical data--> |
||
| C=16 | H=13 | N=3 | O=3 |
| C=16 | H=13 | N=3 | O=3 |
||
| molecular_weight = 295.293 g/mol |
| molecular_weight = 295.293 g/mol |
||
| smiles = O=C(c2cc1c(nc(n1)NC(=O)OC)cc2)c3ccccc3 |
| smiles = O=C(c2cc1c(nc(n1)NC(=O)OC)cc2)c3ccccc3 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| InChI = 1/C16H13N3O3/c1-22-16(21)19-15-17-12-8-7-11(9-13(12)18-15)14(20)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-9H,1H3,(H2,17,18,19,21) |
|||
| InChIKey = OPXLLQIJSORQAM-UHFFFAOYAP |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C16H13N3O3/c1-22-16(21)19-15-17-12-8-7-11(9-13(12)18-15)14(20)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-9H,1H3,(H2,17,18,19,21) |
| StdInChI = 1S/C16H13N3O3/c1-22-16(21)19-15-17-12-8-7-11(9-13(12)18-15)14(20)10-5-3-2-4-6-10/h2-9H,1H3,(H2,17,18,19,21) |
||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{ |
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{Stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| StdInChIKey = OPXLLQIJSORQAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| StdInChIKey = OPXLLQIJSORQAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
||
| melting_point = 288.5 |
| melting_point = 288.5 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''メベンダゾール'''(Mebendazole、MBZ)は、[[ベンゾイミダゾール]]系の[[駆虫薬]]であり、スペクトラムが広い、即ち多くの[[寄生虫]]治療に用いる事の出来る医薬品である<ref name=AHFS2015/>。[[回虫症]]、{{仮リンク|蟯虫感染症|en|pinworm disease}}、{{仮リンク|鉤虫症|en|hookworm infection}}、[[メジナ虫症]]、[[エキノコックス症]]、[[ジアルジア症]]等が有る<ref name=AHFS2015>{{Cite web|title=Mebendazole|url=http://www.drugs.com/monograph/mebendazole.html|publisher=The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists|accessdate=Aug 18, 2015}}</ref>。日本では[[鞭虫症]]治療薬として承認されている<ref name=pi>{{Cite web |date=2011-03 |url=http://www.info.pmda.go.jp/go/pack/6429005F1026_1_07/ |title=メベンダゾール錠100 添付文書 |accessdate=2016-04-21}}</ref>。 |
|||
メベンダゾールの忍容性は高い<ref name=AHFS2015/>。副作用として[[頭痛]]、嘔吐、[[耳鳴り|耳鳴]]が知られている<ref name=AHFS2015/>。高用量を投与すると、{{仮リンク|骨髄抑制|en|bone marrow suppression}}が起こる<ref name=AHFS2015/>。妊婦への安全性は確立していない<ref name=AHFS2015/>。 |
|||
'''メベンダゾール'''('''Mebendazole:MBZ''')は、[[抗寄生虫薬]]の一つ。[[蠕虫]]等に用いられる。 |
|||
1971から実用され始めた<ref>{{Cite book|last1=Mehlhorn|first1=Heinz|title=Encyclopedic reference of parasitology. 107 tables|date=2001|publisher=Springer|location=Berlin [u.a.]|isbn=9783540668299|page=259|edition=2|url=https://books.google.ca/books?id=OBZbR4vpg0YC&pg=PA259}}</ref>。[[WHO必須医薬品モデル・リスト]]に収載されている<ref>{{Cite web|title=WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines|url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/93142/1/EML_18_eng.pdf?ua=1|work=World Health |accessdate=2016-04-21}}</ref>。 |
|||
==効能・効果== |
|||
日本で正式に承認されている効能・効果は「鞭虫症」のみである<ref name=pi/>。 |
|||
メベンダゾールは効果の高い、広範囲に有効な[[駆虫薬]]で、回虫、鉤虫、鞭虫、線虫、蟯虫等の感染症、旋毛虫症(小腸内)の治療に使用される。メベンダゾールは消化管から吸収され難いので、消化管外に寄生した寄生虫には別の薬剤が用いられる<ref name = "Goodman">{{Cite book |author=Petri WA |coauthorsBrunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC= |year=2011 |title=Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th ed. |publisher=McGraw-Hill |page=Chapter 42. |isbn=978-0071624428}}</ref>。メベンダゾールは軽度から中等度の感染症に単剤で使用される。殺虫効果が見られる迄の時間が比較的長く、重症感染症では寄生虫が消化管外に出て虫垂炎、胆管障害、腸穿孔等に繋がる危険が有る。それらの危険を除く為に、重症感染症患者には[[ピペラジン]]を用いるほうが望ましい。ピペラジンは寄生虫を麻痺させ、糞虫に排出させる<ref>{{Cite book |author=Martin AR |coauthors=Doerge RF |year=1982 |title= |
|||
Wilson and Gisvold's Textbook of Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry |publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins |page=Chapter 4 |isbn=978-0397515837}}</ref>。 稀に包虫症の治療にも使用されるが、有効性は充分に証明されていない<ref>{{Cite web|title=Mebendazole|url=http://www.drugs.com/monograph/mebendazole.html|website=drugs.com|accessdate=25 January 2015}}</ref>。 |
|||
メベンダゾールや他のベンズイミダゾール系抗寄生虫薬は、線虫の幼虫及び成虫に有効であり、回虫と鞭虫の場合には、卵に対しても殺虫効果を持つ。寄生虫とその死骸は数日掛けて鞭虫に排出される<ref name = Goodman />。 |
|||
===妊産婦・授乳婦=== |
|||
米国でのメベンダゾールの[[胎児危険度分類]]はCであり、動物実験では妊娠に異常を来たすがヒトでは臨床試験が実施されていない。母乳中に分泌されるか否かは不明である<ref name = Harrison>{{Cite book |author=Finberg R, Fingeroth J in Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo |year=2012 |title=Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 18th ed. |publisher=McGraw-Hill |page=Chapter 217 |isbn=978-0071748896}}</ref>。 |
|||
==副作用== |
|||
重大な副作用として、ショック・アナフィラキシー様症状、中毒性表皮壊死融解症(Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis:TEN)、皮膚粘膜眼症候群(Stevens-Johnson症候群)が知られている<ref name=pi/>。 |
|||
屢々 下痢、腹痛、肝酵素上昇を起こす。稀に、危険な白血球減少及び{{仮リンク|血小板減少|en|thrombocytopenia}}、脱毛を引き起こす<ref name = Harrison /><ref>{{Cite journal |author=Andersohn F, Konzen C, Garbe E |title=Systematic review: agranulocytosis induced by nonchemotherapy drugs |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=146 |issue=9 |pages=657–65 |date=May 2007 |pmid=17470834 |doi=10.7326/0003-4819-146-9-200705010-00009 |url=http://annals.org/article.aspx?articleid=734449}}</ref>。[[無顆粒球症]]が起こる事が稀に有る。 |
|||
===相互作用=== |
|||
[[カルバマゼピン]]や[[フェニトイン]]はメベンダゾールの血中濃度を低下させる。メベンダゾールは血中に殆ど吸収されないので、[[シメチジン]]は明瞭にはメベンダゾールの血中濃度を上昇させない<ref>{{Cite web |
|||
| title = Drug Interactions |
|||
| url = http://www.medicinechestonline.co.uk/static/professional2/drug_interactions.htm |
|||
| publisher = Medicine chest |
|||
| accessdate = 2008-05-06 |
|||
}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |
|||
| author = Luder PJ, Siffert B, Witassek F, Meister F, Bircher J |
|||
| title = Treatment of hydatid disease with high oral doses of mebendazole. Long-term follow-up of plasma mebendazole levels and drug interactions |
|||
| journal = European journal of clinical pharmacology |
|||
| volume = 31 |
|||
| issue = 4 |
|||
| pages = 443–448 |
|||
| year = 1986 |
|||
| pmid = 3816925 |
|||
| doi=10.1007/bf00613522 |
|||
| last2 = Siffert |
|||
| last3 = Witassek |
|||
| last4 = Meister |
|||
| last5 = Bircher |
|||
}}</ref>。これは類薬の[[アルベンダゾール]]とは対照的である。 |
|||
高用量の[[メトロニダゾール]]の併用で[[スティーブンス・ジョンソン症候群]]や{{仮リンク|中毒性表皮壊死融解症|en|toxic epidermal necrolysis}}が発生し得る<ref name="pmid12604501">{{Cite journal |
|||
| author = Chen, K. T.; Twu, S. J.; Chang, H. J.; Lin, R. S. |
|||
| title = Outbreak of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome / Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Mebendazole and Metronidazole Use Among Filipino Laborers in Taiwan |
|||
| journal = American Journal of Public Health |
|||
| volume = 93 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| pages = 489–492 |
|||
| year = 2003 |
|||
| pmid = 12604501 |
|||
| pmc = 1447769 |
|||
| doi=10.2105/ajph.93.3.489 |
|||
}}</ref>。 |
|||
==作用機序== |
|||
メベンダゾールは寄生虫の微小管合成を選択的に阻害し、虫の腸内の既存の細胞質微小管を破壊し、グルコース等の栄養吸収を妨げ、緩やかに虫体を不動化し、死に至らしめる<ref name = Goodman />。 |
|||
==研究開発== |
|||
幾つかの研究で、メベンダゾールが抗腫瘍活性を有する事が示されている。メベンダゾールは有意に腫瘍細胞の成長や転移を阻害し、{{仮リンク|副腎皮質癌|en|adrenocortical carcinoma}}に対して''[[in vitro]]'' と''[[in vivo]]'' の両方で効果を示した<ref name="pmid17581752">{{Cite journal | author = Martarelli D, Pompei P, Baldi C, Mazzoni G | title = Mebendazole inhibits growth of human adrenocortical carcinoma cell lines implanted in nude mice | journal = Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. | volume = 61 | issue = 5 | pages = 809–17 |date=April 2008 | pmid = 17581752 | doi = 10.1007/s00280-007-0538-0 }}</ref>。肺癌系の細胞株を用いた実験では、有糸分裂を停止させ、[[カスパーゼ]]活性化と[[シトクロムc]]放出に因ってアポトーシスを誘導した<ref name="pmid12479701">{{Cite journal | author = Sasaki J, Ramesh R, Chada S, Gomyo Y, Roth JA, Mukhopadhyay T | title = The anthelmintic drug mebendazole induces mitotic arrest and apoptosis by depolymerizing tubulin in non-small cell lung cancer cells | journal = Mol. Cancer Ther. | volume = 1 | issue = 13 | pages = 1201–9 |date=November 2002 | pmid = 12479701 | doi = }}</ref>。メベンダゾールはヒト肺癌細胞株に対して用量・時間依存的にアポトーシスを誘導し<ref name="pmid12231542">{{Cite journal | author = Mukhopadhyay T, Sasaki J, Ramesh R, Roth JA | title = Mebendazole elicits a potent antitumor effect on human cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo | journal = Clin. Cancer Res. | volume = 8 | issue = 9 | pages = 2963–9 |date=September 2002 | pmid = 12231542 | doi = }}</ref>、化学療法抵抗性[[悪性黒色腫]]細胞に対して{{仮リンク|Bcl-2|en|Bcl-2}}を賦活化させてアポトーシスさせた<ref name="pmid18667591">{{Cite journal | author = Doudican N, Rodriguez A, Osman I, Orlow SJ | title = Mebendazole induces apoptosis via Bcl-2 inactivation in chemoresistant melanoma cells | journal = Mol. Cancer Res. | volume = 6 | issue = 8 | pages = 1308–15 |date=August 2008 | pmid = 18667591 | doi = 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2159 }}</ref>。 |
|||
==出典== |
|||
{{Reflist|30em}} |
|||
{{デフォルトソート:めへんたそる}} |
{{デフォルトソート:めへんたそる}} |
||
[[Category:駆虫薬]] |
|||
[[Category:WHOエッセンシャルドラッグ]] |
|||
[[Category:芳香族ケトン]] |
|||
[[Category:抗寄生虫薬]] |
[[Category:抗寄生虫薬]] |
||
[[Category:ベンゾフェノン]] |
[[Category:ベンゾフェノン]] |
||
[[Category:ベンゾイミダゾール]] |
[[Category:ベンゾイミダゾール]] |
||
[[Category:カルバミン酸]] |
[[Category:カルバミン酸]] |
||
{{Pharm-stub}} |
|||
2016年4月20日 (水) 17:53時点における版
 | |
| IUPAC命名法による物質名 | |
|---|---|
| |
| 臨床データ | |
| 販売名 | Vermox[1] |
| Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682315 |
| 胎児危険度分類 | |
| 法的規制 | |
| 投与経路 | Oral |
| 薬物動態データ | |
| 生物学的利用能 | 2-10% |
| 血漿タンパク結合 | 95% |
| 代謝 | Hepatic (extensive) |
| 半減期 | 3-6 hours |
| 排泄 | Faeces, urine (5-10%) |
| 識別 | |
| CAS番号 |
31431-39-7 |
| ATCコード | P02CA01 (WHO) QP52AC09 (WHO) |
| PubChem | CID: 4030 |
| DrugBank |
DB00643 |
| ChemSpider |
3890 |
| UNII |
81G6I5V05I |
| KEGG |
D00368 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:6704 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL685 |
| 化学的データ | |
| 化学式 | C16H13N3O3 |
| 分子量 | 295.293 g/mol |
| |
| 物理的データ | |
| 融点 | 288.5 °C (551.3 °F) |
メベンダゾール(Mebendazole、MBZ)は、ベンゾイミダゾール系の駆虫薬であり、スペクトラムが広い、即ち多くの寄生虫治療に用いる事の出来る医薬品である[2]。回虫症、蟯虫感染症、鉤虫症、メジナ虫症、エキノコックス症、ジアルジア症等が有る[2]。日本では鞭虫症治療薬として承認されている[3]。
メベンダゾールの忍容性は高い[2]。副作用として頭痛、嘔吐、耳鳴が知られている[2]。高用量を投与すると、骨髄抑制が起こる[2]。妊婦への安全性は確立していない[2]。
1971から実用され始めた[4]。WHO必須医薬品モデル・リストに収載されている[5]。
効能・効果
日本で正式に承認されている効能・効果は「鞭虫症」のみである[3]。
メベンダゾールは効果の高い、広範囲に有効な駆虫薬で、回虫、鉤虫、鞭虫、線虫、蟯虫等の感染症、旋毛虫症(小腸内)の治療に使用される。メベンダゾールは消化管から吸収され難いので、消化管外に寄生した寄生虫には別の薬剤が用いられる[6]。メベンダゾールは軽度から中等度の感染症に単剤で使用される。殺虫効果が見られる迄の時間が比較的長く、重症感染症では寄生虫が消化管外に出て虫垂炎、胆管障害、腸穿孔等に繋がる危険が有る。それらの危険を除く為に、重症感染症患者にはピペラジンを用いるほうが望ましい。ピペラジンは寄生虫を麻痺させ、糞虫に排出させる[7]。 稀に包虫症の治療にも使用されるが、有効性は充分に証明されていない[8]。
メベンダゾールや他のベンズイミダゾール系抗寄生虫薬は、線虫の幼虫及び成虫に有効であり、回虫と鞭虫の場合には、卵に対しても殺虫効果を持つ。寄生虫とその死骸は数日掛けて鞭虫に排出される[6]。
妊産婦・授乳婦
米国でのメベンダゾールの胎児危険度分類はCであり、動物実験では妊娠に異常を来たすがヒトでは臨床試験が実施されていない。母乳中に分泌されるか否かは不明である[9]。
副作用
重大な副作用として、ショック・アナフィラキシー様症状、中毒性表皮壊死融解症(Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis:TEN)、皮膚粘膜眼症候群(Stevens-Johnson症候群)が知られている[3]。
屢々 下痢、腹痛、肝酵素上昇を起こす。稀に、危険な白血球減少及び血小板減少、脱毛を引き起こす[9][10]。無顆粒球症が起こる事が稀に有る。
相互作用
カルバマゼピンやフェニトインはメベンダゾールの血中濃度を低下させる。メベンダゾールは血中に殆ど吸収されないので、シメチジンは明瞭にはメベンダゾールの血中濃度を上昇させない[11][12]。これは類薬のアルベンダゾールとは対照的である。
高用量のメトロニダゾールの併用でスティーブンス・ジョンソン症候群や中毒性表皮壊死融解症が発生し得る[13]。
作用機序
メベンダゾールは寄生虫の微小管合成を選択的に阻害し、虫の腸内の既存の細胞質微小管を破壊し、グルコース等の栄養吸収を妨げ、緩やかに虫体を不動化し、死に至らしめる[6]。
研究開発
幾つかの研究で、メベンダゾールが抗腫瘍活性を有する事が示されている。メベンダゾールは有意に腫瘍細胞の成長や転移を阻害し、副腎皮質癌に対してin vitro とin vivo の両方で効果を示した[14]。肺癌系の細胞株を用いた実験では、有糸分裂を停止させ、カスパーゼ活性化とシトクロムc放出に因ってアポトーシスを誘導した[15]。メベンダゾールはヒト肺癌細胞株に対して用量・時間依存的にアポトーシスを誘導し[16]、化学療法抵抗性悪性黒色腫細胞に対してBcl-2を賦活化させてアポトーシスさせた[17]。
出典
- ^ Ebadi, Manuchair (2008). Desk reference of clinical pharmacology (2 ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. 403. ISBN 9781420047448
- ^ a b c d e f “Mebendazole”. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. 2015年8月18日閲覧。
- ^ a b c “メベンダゾール錠100 添付文書” (2011年3月). 2016年4月21日閲覧。
- ^ Mehlhorn, Heinz (2001). Encyclopedic reference of parasitology. 107 tables (2 ed.). Berlin [u.a.]: Springer. p. 259. ISBN 9783540668299
- ^ “WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines”. World Health. 2016年4月21日閲覧。
- ^ a b c Petri WA (2011). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 12th ed.. McGraw-Hill. p. Chapter 42.. ISBN 978-0071624428
- ^ Martin AR; Doerge RF (1982). Wilson and Gisvold's Textbook of Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. Chapter 4. ISBN 978-0397515837
- ^ “Mebendazole”. drugs.com. 2015年1月25日閲覧。
- ^ a b Finberg R, Fingeroth J in Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo (2012). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 18th ed.. McGraw-Hill. p. Chapter 217. ISBN 978-0071748896
- ^ Andersohn F, Konzen C, Garbe E (May 2007). “Systematic review: agranulocytosis induced by nonchemotherapy drugs”. Ann. Intern. Med. 146 (9): 657–65. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-146-9-200705010-00009. PMID 17470834.
- ^ “Drug Interactions”. Medicine chest. 2008年5月6日閲覧。
- ^ Luder PJ, Siffert B, Witassek F, Meister F, Bircher J; Siffert; Witassek; Meister; Bircher (1986). “Treatment of hydatid disease with high oral doses of mebendazole. Long-term follow-up of plasma mebendazole levels and drug interactions”. European journal of clinical pharmacology 31 (4): 443–448. doi:10.1007/bf00613522. PMID 3816925.
- ^ Chen, K. T.; Twu, S. J.; Chang, H. J.; Lin, R. S. (2003). “Outbreak of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome / Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Mebendazole and Metronidazole Use Among Filipino Laborers in Taiwan”. American Journal of Public Health 93 (3): 489–492. doi:10.2105/ajph.93.3.489. PMC 1447769. PMID 12604501.
- ^ Martarelli D, Pompei P, Baldi C, Mazzoni G (April 2008). “Mebendazole inhibits growth of human adrenocortical carcinoma cell lines implanted in nude mice”. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 61 (5): 809–17. doi:10.1007/s00280-007-0538-0. PMID 17581752.
- ^ Sasaki J, Ramesh R, Chada S, Gomyo Y, Roth JA, Mukhopadhyay T (November 2002). “The anthelmintic drug mebendazole induces mitotic arrest and apoptosis by depolymerizing tubulin in non-small cell lung cancer cells”. Mol. Cancer Ther. 1 (13): 1201–9. PMID 12479701.
- ^ Mukhopadhyay T, Sasaki J, Ramesh R, Roth JA (September 2002). “Mebendazole elicits a potent antitumor effect on human cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo”. Clin. Cancer Res. 8 (9): 2963–9. PMID 12231542.
- ^ Doudican N, Rodriguez A, Osman I, Orlow SJ (August 2008). “Mebendazole induces apoptosis via Bcl-2 inactivation in chemoresistant melanoma cells”. Mol. Cancer Res. 6 (8): 1308–15. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2159. PMID 18667591.
