S-アリルシステイン
表示
| S-Allyl cysteine | |
|---|---|
| |
| |
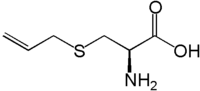
(R)-2-Amino-3-prop-2-enylsulfanylpropanoic acid | |
別称 S-2-propenyl-L-cysteine; S-allyl-laevo-cysteine; S-allylcysteine | |
| 識別情報 | |
| 略称 | SAC |
| CAS登録番号 | 21593-77-1 |
| PubChem | 9793905 |
| ChemSpider | 7969672 |
| UNII | 81R3X99M15 |
| |
| |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C6H11NO2S |
| モル質量 | 161.22 g/mol |
| 密度 | 1.191 ± 0.06 g/cm3 |
| 融点 |
219 to 220 °C, 構文エラー:「to」を認識できません。 K, 構文エラー:「to」を認識できません。 °F |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
S-アリルシステインは、タンパク質が分解されたものでアミノ酸の一種である[1]。
イオウ原子を含む無臭であるのが特長であり、酵素反応によってできる水溶性化合物である。
同成分を多く含む食品としては、黒ニンニクが代表的であるが、黒ニンニクに加工する前のニンニクには、ほとんど含まれていない。
ニンニクが含むガンマ-グルタミル-S-アリルシステインという成分が、酵素の働きを受けて、S-アリルシステイン変化する。
効能としては、抗酸化作用が一般的に言われている[2] and as a chemopreventive.[3] 。
概要[編集]
この節の加筆が望まれています。 |
脚注[編集]
- ^ Fujii, Takuto; Matsutomo, Toshiaki; Kodera, Yukihiro (2018). “Changes of S-Allylmercaptocysteine and γ-Glutamyl-S-allylmercaptocysteine Contents and Their Putative Production Mechanisms in Garlic Extract during the Aging Process”. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 66 (40): 10506–10512. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02541. PMID 30226990.
- ^ “Cholesterol-lowering effect of garlic extracts and organosulfur compounds: human and animal studies”. Journal of Nutrition 131 (3s): 989S–93S. (2001). doi:10.1093/jn/131.3.989S. PMID 11238803.
- ^ Arora, Annu; Tripathi, Chitra; Shukla, Yogeshwer (2005). “Garlic and its organosulfides as potential chemopreventive agents: a review”. Current Cancer Therapy Reviews 1 (2): 199–205. doi:10.2174/1573394054021772.
