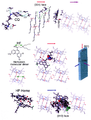
English: Top row. Binding of chloroquine (CQ) to the {001} and {100} faces of hemozoin (HZ). (Left) Electrostatic interactions between CQ and HZ at the {001} face, including base-acid N(CH2CH3)2-H+…-O2C, acceptor-donor (ring)N…H-C(H)=CH-, acceptor-donor (quinoline)Cl…H3C- and proton donor-p(acceptor) (exocyclic)N-H…H2C=CH .(Center). CQ intercalated within groove, delineated by dashed green line, on surface of {001} face, viewed edge-on along the a-crystal axis. Binding of CQ to the {100} face of HZ.
Central row. Binding of halofantrine (HF) to the {001} and {010} faces of HZ
(Left, top) Molecular structure of HF. The double-arrow denotes the separation between the tertiary N and the OH group. (Left, bottom) Cyclic heme dimer in crystal structure of HZ, where the double-arrow denotes the separation between the propionic acid group and the Fe carboxylate carbonyl group. (Center) binding of HF to the {001} face of HZ viewed face-on. HF is too bulky to be intercalated within a groove on the }001} face as is CQ. Nevertheless, HF forms strong interactions with the }001} surface; the OH group of HF is hydrogen bonded to the Fe-carboxylate carbonyl O atom and the tertiary N-H+ group is H-bonded to the CO2- group of HZ. Note HF can bind to the {100} face of HZ in an arrangement akin to that of CQ to the {100} face of HZ, see top row, right.
Bottom row. Binding of HF-heme coordination complex to the {010} face of hemozoin.
(Left) Molecular structure of the HF-ferriprotoporphyrin IX coordination complex (K. A. de Villiers, H. M. Marques, T. J. Egan, J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1660). (Right) Binding of the HF-Heme complex to the {010} face of hemozoin, where the HF moiety of the complex emerges from the crystal face. The {010} face is viewed edge-on, along the c-axis. Note that the quinoline methanols, such as quinine and mefloquine also form coordination complexes with ferriproto-porphyrin IX, according to Egan and coworkers. Thus such quinoline-heme complexes can also be adsorbed onto the {010} face.
Note that the red, violet and blue arrows drawn above the drug-hemozoin arrangements and on the crystal faces shown in central row, right, designate attachment of the particular antimalarial drug to the {001}, {100} and {010} faces respectively, and subsequent inhibition.