「1回換気量」の版間の差分
表示
削除された内容 追加された内容
Anesth Earth (会話 | 投稿記録) ページ「Tidal volume」の翻訳により作成 |
Anesth Earth (会話 | 投稿記録) 表を{{Pulmonoary function}}に貼り替え |
||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
{{Pulmonary function}} |
|||
{| class="infobox" |
|||
| colspan="2" class="infobox-image" |[[File:Lungvolumes_Updated.png|フレームなし]] |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |TLC |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Total lung capacity: the volume in the lungs at maximal inflation, the sum of VC and RV. |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |TV |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs in 1 breath (TV indicates a subdivision of the lung; when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or V<sub>T</sub> is used.) |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |RV |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Residual volume: the volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalation |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |ERV |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Expiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume of air that can be exhaled from the end-expiratory position |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |IRV |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Inspiratory reserve volume: the maximal volume that can be inhaled from the end-inspiratory level |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |IC |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Inspiratory capacity: the sum of IRV and TV |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |IVC |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Inspiratory vital capacity: the maximum volume of air inhaled from the point of maximum expiration |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |VC |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Vital capacity: the volume of air breathed out after the deepest inhalation. |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |V<sub>T</sub> |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Tidal volume: that volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing (VT indicates a subdivision of the lung; when tidal volume is precisely measured, as in gas exchange calculation, the symbol TV or V<sub>T</sub> is used.) |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |FRC |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Functional residual capacity: the volume in the lungs at the end-expiratory position |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |RV/TLC% |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Residual volume expressed as percent of TLC |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |V<sub>A</sub> |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Alveolar gas volume |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |V<sub>L</sub> |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Actual volume of the lung including the volume of the conducting airway. |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |FVC |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Forced vital capacity: the determination of the vital capacity from a maximally forced expiratory effort |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |FEV<sub>t</sub> |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Forced expiratory volume (time): a generic term indicating the volume of air exhaled under forced conditions in the first ''t'' seconds |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |FEV<sub>1</sub> |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Volume that has been exhaled at the end of the first second of forced expiration |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |FEF<sub>x</sub> |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Forced expiratory flow related to some portion of the FVC curve; modifiers refer to amount of FVC already exhaled |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |FEF<sub>max</sub> |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |The maximum instantaneous flow achieved during a FVC maneuver |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |FIF |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Forced inspiratory flow: (Specific measurement of the forced inspiratory curve is denoted by nomenclature analogous to that for the forced expiratory curve. For example, maximum inspiratory flow is denoted FIF<sub>max</sub>. Unless otherwise specified, volume qualifiers indicate the volume inspired from RV at the point of measurement.) |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |PEF |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Peak expiratory flow: The highest forced expiratory flow measured with a peak flow meter |
|||
|- |
|||
! class="infobox-label" scope="row" |MVV |
|||
| class="infobox-data" |Maximal voluntary ventilation: volume of air expired in a specified period during repetitive maximal effort |
|||
|- |
|||
| colspan="2" class="infobox-navbar" |<templatestyles src="Hlist/styles.css"></templatestyles><templatestyles src="Module:Navbar/styles.css"></templatestyles> |
|||
|} |
|||
'''1回換気量'''(いっかいかんきりょう、{{Lang-en-short|tidal volume}}、記号'''V<sub>T</sub>''' または'''TV''')とは、1回の[[呼吸]]で肺に出入りする空気の量のことである<ref>{{Citation|title=Physiology, Lung|last=Haddad|first=Moshe|last2=Sharma|first2=Sandeep|date=2021|url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545177/|journal=StatPearls|publisher=StatPearls Publishing|location=Treasure Island (FL)|pmid=31424761|access-date=2021-03-17}}</ref>。健康で若い成人の場合、安静時の1回の吸気量は約500ml、または理想体重1kgあたり7mlである。 |
'''1回換気量'''(いっかいかんきりょう、{{Lang-en-short|tidal volume}}、記号'''V<sub>T</sub>''' または'''TV''')とは、1回の[[呼吸]]で肺に出入りする空気の量のことである<ref>{{Citation|title=Physiology, Lung|last=Haddad|first=Moshe|last2=Sharma|first2=Sandeep|date=2021|url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545177/|journal=StatPearls|publisher=StatPearls Publishing|location=Treasure Island (FL)|pmid=31424761|access-date=2021-03-17}}</ref>。健康で若い成人の場合、安静時の1回の吸気量は約500ml、または理想体重1kgあたり7mlである。 |
||
2024年5月19日 (日) 06:35時点における版
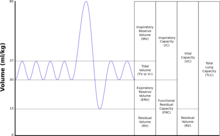 | |
| TLC | 全肺気量(Total Lung Capacity):最大膨張時の肺の容積で、肺活量(VC)と残気量(RV)の合計。 |
|---|---|
| TV (VT) | 1回換気量(Tidal Volume):安静時呼吸で肺に入る、または肺から出る空気の量(TVは肺の区分を示す。ガス交換計算のように1回換気量を正確に測定する場合は、TVまたはVTという記号を用いる)。 |
| RV | 残気量(Residual Volume):最大呼気後に肺に残っている空気の体積 |
| ERV | 予備呼気量(Expiraroty Reserve Volume):安静呼気位から吐き出すことができる最大の呼気量 |
| IRV | 予備吸気量(Inspiratory Reserve Volume): 安静吸気位から吸うことが出来る最大の吸気量 |
| IC | 最大吸気量(Inspiratory Capacity): 予備吸気量(IRV)と1回換気量(TV)の合計 |
| IVC | 吸気肺活量(Inspiratory Vital Capacity): 最大呼気位から吸うことが出来る最大の空気の量 |
| VC | 肺活量(Vital Capacity):最も深く息を吸った後に吐き出される空気の量 |
| FRC | 機能的残気量(Functional Residual Capacity ):呼気終末位での肺容積 |
| RV/TLC% | 残気量・全肺気量比 |
| VA | 肺胞気量(Alveolar gas Volume) |
| VL | 気道の容積を含む肺の実容積 |
| FVC | 努力肺活量(Forced vital capacity): 最大強制呼気努力による肺活量測定 |
| FEVt | 強制呼気量(Forced expiratory volume (time)): 最初の「t秒」に強制的に吐き出される空気の量の総称 |
| FEV1 | 1秒量(Forced expiratory volume (1 second)): 強制呼気の最初の1秒が終了した時点で吐き出された量 |
| FEFx | FVC曲線の一部に関連する強制呼気流量、修飾子はすでに吐き出されたFVCの量を指す |
| FEFmax | FVC測定時に達成される最大瞬時流量 |
| FIF | 強制吸気流量( Forced inspiratory flow): 強制吸気曲線の具体的な測定値は、強制呼気曲線に類似した命名法で示される。例えば、最大吸気流量はFIFmaxと表記される。特に指定がない限り、体積の修飾子は、測定時点の残気量から吸入される体積を示す。 |
| PEF | 最大呼気流量(Peak expiratory flow):ピークフローメーターで測定した強制呼気流量の最高値。 |
| MVV | 最大換気量(Maximal voluntary ventilation): 一定の時間に最大努力で繰り返して呼出できる空気の量 |
1回換気量(いっかいかんきりょう、英: tidal volume、記号VT またはTV)とは、1回の呼吸で肺に出入りする空気の量のことである[1]。健康で若い成人の場合、安静時の1回の吸気量は約500ml、または理想体重1kgあたり7mlである。
機械換気における1回換気量
1回換気量の設定は、肺に損傷を与えることなく十分な換気を確保するために、人工呼吸中に重要な役割を果たす。1回換気量はミリリットル単位で測定され、換気量は患者の理想体重に基づいて設定される。1回換気量の測定は、呼吸回路の漏れや、例えばネブライザーによる薬剤導入時の追加ガスの導入によって影響を受けることがある。
急性肺障害(ALI)/急性呼吸窮迫症候群(ARDS)のような人工呼吸器誘発性肺損傷は、たとえ、正常肺であっても非常に大きな1回換気量での換気、および既に病変のある肺における中等度または少量の1回換気量での換気によって引き起こされる可能性がある。神経学的障害のない患者では、1回換気量を大きく設定するほどALIの発生率が増加することが研究で示されている[2]。.同様に、コクランによる2018年のシステマティックレビューでは、低1回換気量換気が術後肺炎を減少させ、術後の侵襲的換気および非侵襲的換気の必要性を減少させるというエビデンスが示されている[3]。
脚注
出典
- ^ Haddad, Moshe; Sharma, Sandeep (2021), “Physiology, Lung”, StatPearls (Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing), PMID 31424761 2021年3月17日閲覧。
- ^ Gajic, Ognjen; Saqib Dara; Jose Mendez; Abedola Adensanya; Emir Festic; Sean Caples; Rimki Rana; Jennifer StSauver et al. (2004). “Ventilator-associated lung injury in patients without acute lung injury at the onset of mechanical ventilation”. Critical Care Medicine 32 (9): 1817–1824. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000133019.52531.30. PMID 15343007.
- ^ Guay, Joanne; Ochroch, Edward A; Kopp, Sandra (2018-07-09). “Intraoperative use of low volume ventilation to decrease postoperative mortality, mechanical ventilation, lengths of stay and lung injury in adults without acute lung injury”. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 7 (10): CD011151. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd011151.pub3. ISSN 1465-1858. PMC 6513630. PMID 29985541.
外部リンク
- Ricard JD (May 2003). “Are we really reducing tidal volume—and should we?”. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 167 (10): 1297–8. doi:10.1164/rccm.2303003. PMID 12738592.
