ファイル:Eunectes-murinus -Broghammerus-reticulatus- -Titanoboa-2.svg
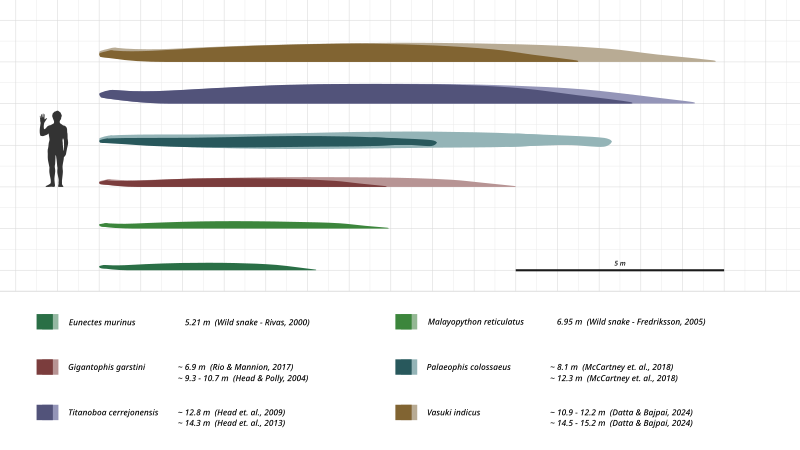
この SVG ファイルのこの PNG プレビューのサイズ: 800 × 267 ピクセル. その他の解像度: 320 × 107 ピクセル | 640 × 213 ピクセル | 1,024 × 341 ピクセル | 1,280 × 427 ピクセル | 2,560 × 853 ピクセル | 1,440 × 480 ピクセル。
元のファイル (SVG ファイル、1,440 × 480 ピクセル、ファイルサイズ: 182キロバイト)
ファイルの履歴
過去の版のファイルを表示するには、その版の日時をクリックしてください。
| 日付と時刻 | サムネイル | 寸法 | 利用者 | コメント | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 現在の版 | 2019年4月24日 (水) 10:55 | 1,440 × 480 (182キロバイト) | Steveoc 86 | Typo - 14.9 to 14.3 | |
| 2019年4月22日 (月) 20:52 | 1,440 × 480 (182キロバイト) | Steveoc 86 | Update diagram, add grid, add colours, and add Gigantophis. | ||
| 2018年5月5日 (土) 12:32 | 1,631 × 346 (16キロバイト) | Oryctolagus XL | . | ||
| 2018年5月1日 (火) 20:34 | 1,600 × 214 (16キロバイト) | Oryctolagus XL | Softer shapes and better head for the python. | ||
| 2018年4月29日 (日) 21:49 | 1,590 × 231 (28キロバイト) | Oryctolagus XL | User created page with UploadWizard |
ファイルの使用状況
以下のページがこのファイルを使用しています:
グローバルなファイル使用状況
以下に挙げる他のウィキがこの画像を使っています:
- ca.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- cs.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- en.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- he.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- hu.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- it.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- ml.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- nl.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- pt.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- th.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- tr.wikipedia.org での使用状況
- www.wikidata.org での使用状況
- zh.wikipedia.org での使用状況
